Applications of bispecific antibodies beyond tumorsPosted by beauty33 on August 13th, 2019 As more and more people begin to focus on bispecific antibodies, more companies and research institutes are conducting related studies. In the development of antibody drug compounds, bispecific antibodies have now accounted for about 20% of the share. Among them, about 68% of the drug candidates are concentrated in the tumor field, and about 50% of which are targeting on CD3.
Figure 1. A structure demonstration of bispecific antibodies (Bsab) Two products are currently market available, namely Catumaxomab, which was launched in 2009, and Blinatumomab, which was launched in 2014. As a pioneer, their market performance of the two is not too bright. This may be because of the "congenital deficiency" of the two. Catumaxomab, as a chimeric antibody to mice and rats, is now unable to keep up with the trend of the times. While Amgen's Blinatumomab was first approved by the FDA for the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-negative precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-cellALL), its poor market performance is mainly due to the small number of indications. But it’s not our focus here in this article. We’re going to review other applications of bispecific antibodies in addition to tumor immunotherapy.
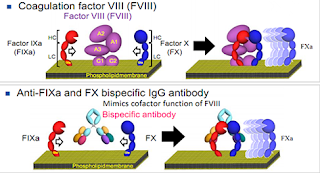
1.1 Emicizumab Emicizumab, developed by Roche/Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. to treat hemophilia A, will be the first non-tumor bispecific antibody if approved. Emicizumab binds both FIXa and FX and pulls the two proteins together to activate the downstream coagulation signaling pathway. It fully mimicked the role of FVIII in the body (Figure 2). Currently, FVIII is the main drug for the treatment of hemophilia, but after long-term use of drugs, about 30% of patients will produce antibody FVIII antibodies, and these patients are in urgent need of new drugs. The emergence of Emicizumab is just right to meet the needs of these patients.
Figure 2. The role of FVIII in the body 1.2 RG-7992 (Roche / Genentech) RG-7992, developed by Roche/Genentech's, provides a method for the use of another bispecific antibody. First, scientists discovered that anti-FGFR1 (anti-fibroblast growth factor receptor 1) antibodies stimulate brown adipose tissue activity, which can increase energy consumption and eliminate excess calorie energy in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. However, since FGFR1 is widely present in various tissues of human body, a single anti-FGFR1 antibody has many side effects caused by off-target, and causes hypophosphatemia in mice. By making bispecific antibodies combined with anti-FGFR1 and KLB (co receptor & beta; klotho), both can mimic FGF21 to reduce blood sugar and blood lipids, and improve insulin resistance, protect islets and beta cells, and other glycolipid metabolism. Currently, this drug candidate has been used in the first phase of clinical practice in type 2 diabetes.
Most bispecific antibodies act like a "double-headed snake" that uses two heads to grasp two different target molecules in the blood circulation. For example, MDG-010, developed by MacroGenic on its own DART technology platform, can simultaneously bind CD32B and CD79B on the surface of B cells, and when they bind to each other, it will initiate a signal that inhibits B cell activity. It is expected that a similar or better clinical effect of rituximab targeting CD20 can be achieved in the treatment of RA. Since the goal of clearing B cells is not targeted, the theoretical side effects will be smaller. In June of this year, the company released a phase I clinical data, which provided strong support for the continued advancement of MDG-010. In addition, BIOCAD's BCD-121 can also "catch" IL-17 and TNF at the same time. It’s no doubt that this model will be a good one, but there are also different opinions that it is not convenient to adjust the organic synthesis of the drug amount in real time according to the disease state compared with the combination of the two drugs.
AstraZeneca's MEDI-3902 provides another application that recognizes Pseudomonas aeruginosa by combining the Pseudomonas aeruginosa surface polysaccharide, Psl, and enriches it on the surface of the cells. It is well known that Pseudomonas aeruginosa can kill nearby immune cells by secreting toxins. Therefore, another target of MEDI-3902 is PcrV against the three-type toxin secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which blocks the release of bacterial toxin by neutralizing PcrV. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which has been cut off toxin release function, becomes “quiet”. At this time, the Fc region of the antibody binds to immune cells, especially macrophages, to remove bacteria. At present, MEDI-3902 is mainly aimed at drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In the era when bacterial resistance has caused great concern and panic, whether MEDI-3902 can finally overcome drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa is worth waiting.
As antibody drugs continue to plague in Alzheimer's disease, many researchers began to reflect whether it is because antibodies are difficult to pass the blood-brain barrier, resulting in too few effective drugs in the brain. In light of this thinking, many companies have begun to target the use of antibodies to carry drugs across the blood-brain barrier: Trojan horse bispecific antibodies. It locks the central nervous system disease. For example, Genentech aimed at Alzheimer's disease, and TfR-knock-in mice and monkeys confirmed that anti-TfR/BACE1 antibodies can effectively reduce the content of amyloid-β (Aβ) in the brain without adverse effects; Angiochem ANG4043 crosses the blood-brain barrier by binding to the LRP-1 receptor; develops Hunter's syndrome in the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs), currently in phase I clinical phase.
In addition to the above, Ablynx has also pioneered a new application. In order to increase the half-life of Nano-antibodies on the product line, Ablynx designed two arms of the bispecific antibody to bind albumin, so that when the antibody enters the bloodstream, it will first bind to albumin in the blood, and then find its own target, in this way to enhance the half-life of the nanobody drug.
At present, bispecific antibodies have been increasingly recognized, and in addition to being directly used in combination with tumor immunotherapy, other applications are more wide spreading. And all kinds of novel ideas are constantly emerging. Like it? Share it!More by this author |